
To distinguish between “aspheric” and “spheric”, why to make it “perfect”?
Source:
Publish time:
2025-09-26
To distinguish between “aspheric” and “spheric”, why to make it “perfect”?
When you with high myopia go to the optician's to choose a pair of glasses, the slim and lightweight lenses matched with various fashionable frames is totally no problem; when you take pictures with a light and handy wide-angle zoom camera or a smartphone, the outstanding image quality with detailed clarity is instantly captured; when you use VR/AR devices, the lifelike images put you right in the scene, all these are the great work of aspheric lenses! Lidar, HUD head up display, laser processing, medical endoscope, 5G communication, infrared thermometer... more or less, aspheric lenses are used in these applications and scenarios. Nowadays, aspheric lenses have stepped into every aspect of our life.
What is an aspheric lens?
In 1638, Johannes Kepler experimented with aspheric surfaces on lenses, obtaining image planes free of spherical aberration at both near and far distances, thereby gradually laying the foundation of aspheric optics.
An aspheric lens refers to an optical element whose surface is determined by a higher‑order polynomial equation, so that the radius of curvature varies from point to point on the surface. When light rays strike an aspheric lens surface, they can be focused to a single point and various aberrations can be eliminated, producing high‑quality optical images. The specific higher‑order polynomial equation is given as follows:
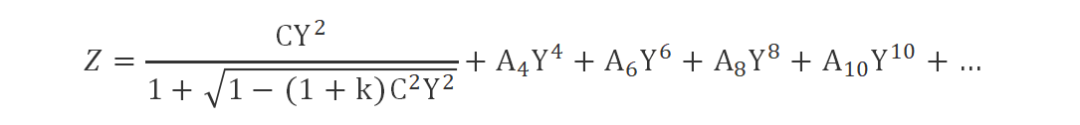
(This formula expresses the surface as a deviation from a conic surface. Z is the surface sag (sagitta), Y is the ray height, C is the curvature of the surface on the optical axis, A4, A6, A8… are the 4th, 6th, 8th… order aspheric coefficients, and k is the conic constant. The relation between k and the aspheric shape is as follows:)
k (conic constant) — Aspheric shape
k = 0 — Sphere
k = −1 — Paraboloid
k < −1 — Hyperboloid
−1 < k < 0 — Ellipsoid (focus on the optical axis)
k > 0 — Ellipsoid (focus lies on a straight line perpendicular to the optical axis)
Differences between Aspheric Lenses and Spherical Lenses
Spherical lenses have various aberrations that cannot be eliminated by a single spherical lens. However, a single aspheric lens can correct various aberrations such as spherical aberration, coma, astigmatism, and field curvature, and reduce light energy loss, thereby achieving high‑quality imaging and optical properties. Below, we will analyze the differences in focusing performance between a single spherical lens and an aspheric lens using a specific example. For the same design wavelength of 532 nm and a focal length of 50 mm, the comparison of the output spot is as follows:
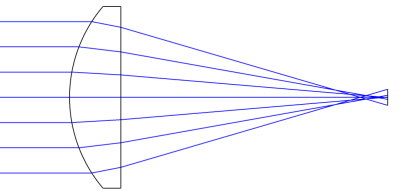
The converging spot of a spherical lens
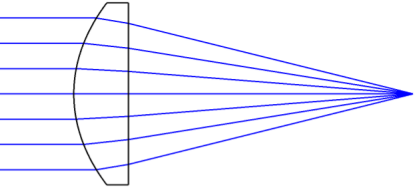
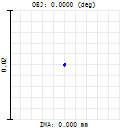
The converging spot of an aspheric lens
In addition, from a system design perspective, aspheric lenses offer advantages over spherical systems: they enable simpler optical structures, wider fields of view, and sharper image quality. Below, we illustrate the superiority of aspheric lenses using a Cooke triplet lens design example.
As shown in the figure below, under the same 30° field-of-view design condition, an optical simulation was performed to image the CASTECH campus. By simply replacing only the fifth surface among the three lenses with an aspheric surface, we achieved significantly reduced edge distortion, improved image sharpness, and a result that more closely resembles the real scene.
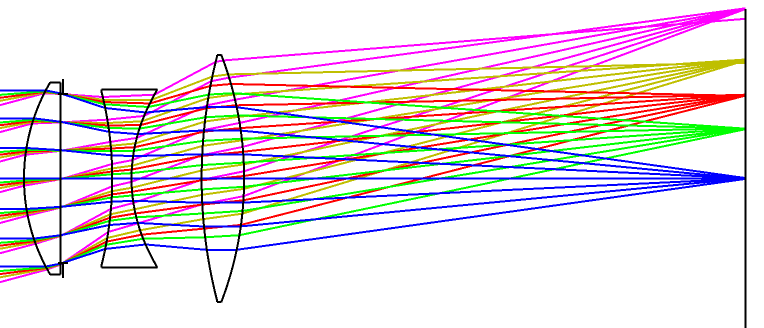
The figure of the Cooke triplet objective lens


Comparison of imaging quality with the 5th surface replaced by an aspheric surface
However, even with the superior performance of aspheric lenses, they are not without challenges. The unique and complex surface shapes, along with the high precision requirements, make them difficult to manufacture industrially. CASTECH has addressed these manufacturing bottlenecks with advanced CNC machining and inspection technologies, enabling the production of high-quality aspheric lenses and aspheric cylindrical lenses.
CNC Machining and Inspection Technologies for Aspheric Lenses
CASTECH has established an advanced, high-precision aspheric CNC machining and testing center, equipped to design, manufacture, and inspect high-precision aspheric lenses and aspheric cylindrical lenses for laser and precision optics applications.
Through iterative CNC polishing and non-contact testing, facilitated by sophisticated computer programs at the machining and testing center, CASTECH achieves high-precision aspheric lenses and aspheric cylindrical lenses. The center offers:
- Diameter Range: From φ5 to φ200 mm
- Surface Quality: Better than 20/10
- Surface Irregularity: Better than λ/4
Standard and Custom Products
The center provides a range of standard and custom aspheric products, meeting the stringent requirements of various optical applications.
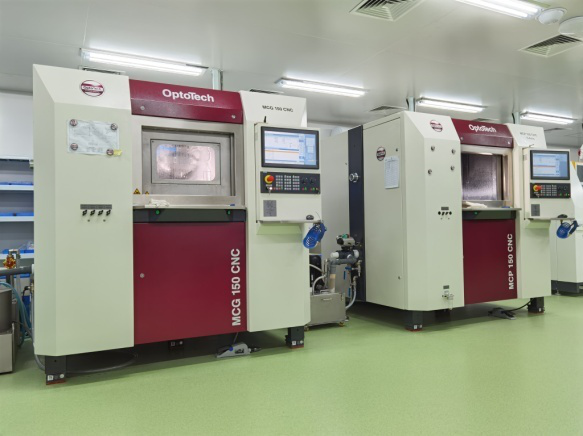

Aspheric CNC machining and testing center
High-precision measurement equipment serves as the "eyes" for high-precision aspheric lens manufacturing. CASTECH employs:
For Precision Grinding:
- Taylor Hobson PGI Optics contact measurement system
For Polishing:
- LuphoScan 260 non-contact measurement system
- Testing aperture: Up to φ260 mm
- Testing accuracy: ±50 nm
These advanced metrology tools ensure the highest quality control throughout the aspheric lens manufacturing process.

PGI Optics contact measurement system

LuphoScan 260 non-contact measurement system
Ion Beam Figuring (IBF) Technology for Aspheric Lenses
CASTECH is equipped with an advanced Ion Beam Figuring (IBF) processing center, complemented by high-precision non-contact metrology systems. By importing aspheric surface measurement data into a computer, the software precisely simulates and controls the ion beam's dwell time in specific areas, enabling rapid, high-performance polishing. This technology achieves aspheric lenses with surface irregularity better than λ/10.
Stay tuned for our upcoming introduction to CASTECH’s Ion Beam Processing Center—more details coming soon!
Related Information




