
PRODUCTS
MESSAGES

Yb:CALGO - Ytterbium Doped Calcium Gadolinium Aluminate
Keyword:
Yb:CALGO - Ytterbium Doped Calcium Gadolinium Aluminate
Category:
- Description
- Cas'Tech Class
- Parameters
-
Introduction
Ytterbium Doped Calcium Gadolinium Aluminate (Yb:CaGdAlO4 or Yb:CALGO) is a promising new laser gain material which possess several important advantages. The crystal structure of CALGO is tetragonal. When it is pumped at 979 nm under π configuration, we can get broad emission spectra from 994 nm to 1050 nm in σ configuration. This implies a very low quantum defect (down to 1.5%) and gives a good expectation of obtaining ultra-fast pulse. In addition, Yb:CALGO also has a thermal conductivity of up to k=6.7 W/m/K, making it suitable for high-power laser applications.
CASTECH’s Yb:CaGdAlO4 is featured by
• High absorption coefficient @979 nm
• High stimulated emission cross section
• Low laser threshold
• Extremely low quantum defect
• Broad output @994-1050 nm
• High slope efficiency with diode pumping (up to 55%)
• Various Yb-doping concentration
• Customizable heat sink assembly
Applications
• Over 5.5 W output power is obtained by 23 W incident pumping diode laser with 10% output coupler;
• Output power as high as 12.5 W and 94 fs pulses for 28 W pumping power was reported.
Table 1. Basic Properties
Crystal Structure Tetragonal Point group I4/mm Lattice Parameter a = 3.6585 Å, c = 11.978 Å Melting Point 1850 ℃ Mohs Hardness 6 Mohs Density 4.8 g/cm3 Thermal Conductivity K[001] = 6.3 W/m/K, K[100] = 6.9 W/m/K Thermal Expansion Coefficients 10.1×10-6 /K (∥a), 16.2 ×10-6 /K (∥c) Laser Wavelength 994-1050 nm Absorption Wavelength 979 nm Absorption Cross Section
(π configuration at 979 nm)
2.7×10-20 cm2 Table 2. Specifications of Yb: CaGdAlO4
Orientation a or c Standard Dopant Concentration Yb: 1, 2, 3, 5 at.% Maximum Length 50 mm Surface Quality (Scratch/Dig) 10/5 to MIL-PRF-13830B Dimensional Tolerances Diameter: ±0.1mm
Length: ±0.5 mm
Parallelism 20 arc sec Perpendicularity ≦15 arc min Coating AR-1030/980 nm,
R<0.2% @1030 nm, R<0.5% @980 nm.
Other coatings are available upon request.
Key words:- laser crystal
- Yb:CALGO
- Yb:CaGdAlO4
- ultra-short pulse
- low quantum defect
-
Cas’Tech Class | Yb:CALGO crystal, a new promising laser crystal for high power ultrafast laser applications
I. Ultrafast laser
It is well known that the laser, one of the greatest inventions of the 20th century, has been described as "the brightest light", "the most accurate ruler" and "the fastest knife "[1]. So what’s ultrafast lasers?
To understand ultrafast lasers, we must know what a laser pulse is. A laser pulse is a pulse of light emitted by a laser that works in a pulse mode. To give an analogy, a torch works continuously if the switch is kept on. And if the switch is turned on and off immediately, it is equivalent to emitting a pulse of light.
A laser pulse can be very short, in the scale of nanosecond, picosecond, femtosecond and even attosecond. The picosecond scale, for example, means that one trillion ultra-short pulses can be emitted in just one second. Generally speaking, a laser with a pulse width of less than 10 ps is called an ultrafast laser.
Table 1 shows the unit of laser pulse width and the conversions.
Table 1: The unit of laser pulse width and the conversions
Unit
Conversion
1ms (millisecond)
10-3 s
1us (microsecond)
10-6 s
1ns (nanosecond)
10-9 s
1ps (picosecond)
10-12 s
1fs (femtosecond)
10-15 s
1as (attosecond)
10-18 s
II. Laser crystals for ultrafast lasers
Currently, there are two main types of laser crystals for ultrafast lasers, namely titanium gemstone (Ti:Al2O3) crystals and Yb3+ ion doped laser crystals. With the development of diode laser (LD) directly pumped all-solid-state lasers (DPSSL) towards high efficiency, miniaturization and integration, Yb3+ ion-doped laser crystals have gradually become a hot spot for ultrafast laser research [1].
Yb3+ ion-doped disordered crystals combine the orderliness of crystals with the disorderliness of glasses and exhibit excellent spectroscopic properties. Among the Yb3+ ion-doped disordered crystals, aluminate crystals are undoubtedly the best comprehensive of all Yb3+ ion-doped ultrafast crystals [2].
Yb:CaGdAlO4 (CALGO) has a tetragonal crystal structure, in which the Ca2+ and Gd3+ ions not only with different ionic radii but also different valence states. So the disorder can be divided into two main categories: disorder in the anion-cation bond length and disorder in the valence distribution[1]. Broaden Yb-emission band caused by multiple disorders makes Yb:CALGO crystal standing out from all the other disordered structured laser crystals[2]. Emission spectral width and thermal conductivity are two key factors while choosing laser crystals for ultrafast lasers. The larger the emission spectral width, the smaller pulse width it gets. And the better the thermal conductivity, the higher the output power it yields. A comparison of the thermal conductivity and emission spectral widths of different Yb-doped laser crystals[3-5] are shown in Table 2.
Table 2: Comparison of thermal conductivity and emission spectral width of different Yb-doped laser crystals
Yb-doped laser crystals
Thermal conductivity
(W.m-1.k-1)
Emission spectrum width
(nm)
Yb:YAG
13
9
Yb:KYW
3.3
24
Yb:KGW
2.6 (a)
3.4 (c)
20
Yb:CaF2
9.71
70
Yb:CALGO
6.9 (a)
6.3 (c)
80
High thermal conductivity and ultra-wide emission spectrum both make Yb:CALGO a promising laser crystal for high power ultrafast laser applications.
III. The history of Yb:CALGO crystals developed by Castech Inc.
CASTECH has started the growth of Yb:CALGO crystals in 2016. In the early stages, the crystal boules were orange in colour and had cloudlike conclusions in most areas (ideally colourless with few conlusion), see Figure 1.

Fig. 1 Yb:CALGO crystal boule with orange color and cloudlike conclusions grown in early stage
The additional unwanted absorption caused by the presence of colour centers and the scattering effect of the inclusions, made Yb:CALGO crystals’ performance by then unable to meet market expectation in terms of laser power and damage threshold. With continuous efforts of CASTECH’s R&D team by making indepth research and repeated experiments on molar ratio, growth temperature field and growth atmosphere, CASTECH can now stably grow colourless, low inclusion level Yb:CALGO crystal boules with dimensions up to dia.30 x 50 mm3 in a stable manner (see Figure 2).
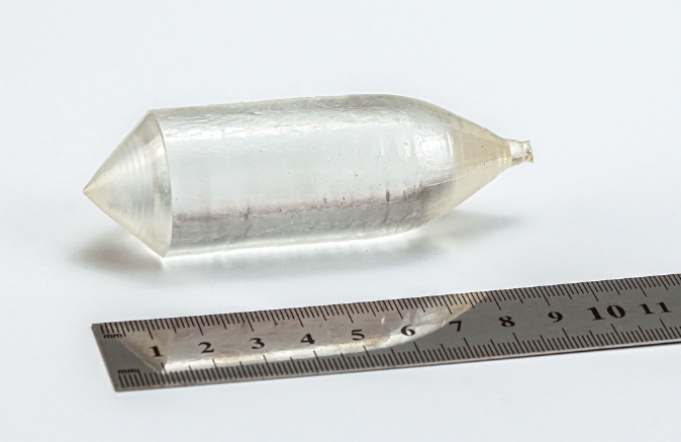

Fig. 2 Colourless Yb:CALGO crystal boule with few inclusions grown currently
The comparison between the colourless (with few inclusions) samples and orange sample (with cloudlike inclusions) in terms of transmittance, output power and laser induced damage threshold shown in Figures 3, 4 and 5, respectively, reflects that there is significant improvement in performance in above aspects.
Transmittance curves (E//C, sample thickness 1.2mm)
------Colourless sample,with few inclusions
----- Orange sample with cloudlike inclusions
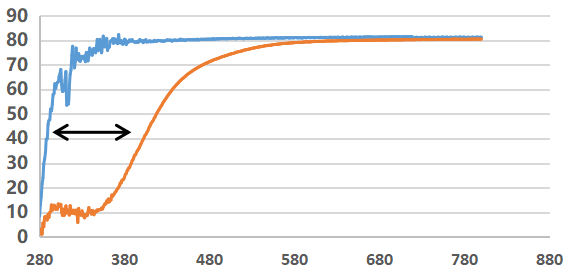
Wave length (nm)
Figure. 3 Comparison of the transmittance curves of the Yb:CALGO crystal samples before and after improvement
Comparison of output power
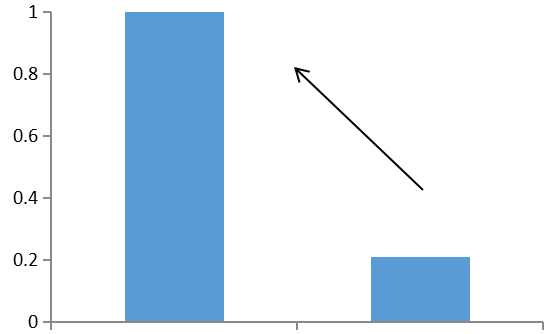
Colourless sample,with few inclusions Orange sample with cloudlike inclusions
Fig. 4 Comparison of the output power of Yb:CALGO crystal samples before and after improvement
Comparison of damage threshold
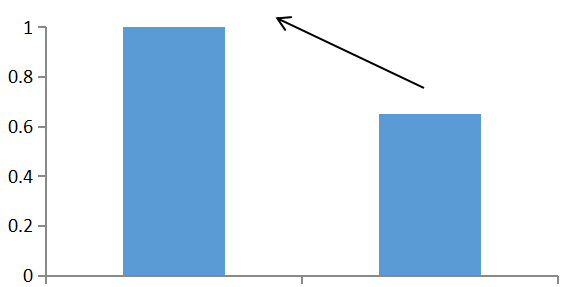
Colourless sample,with few inclusions Orange sample with cloudlike inclusions
Fig. 5 Comparison of damage thresholds of Yb:CALGO crystal samples before and after improvement
IV. Product specifications of Yb:CALGO crystals
Now CASTECH supplies large quantities CALGO crystal components doped with different Yb3+ ion concentrations steadily, with specifications as shown in Table 3.
Table 3: Specifications of Yb:CALGO
Orientation
a or c
Standard dopant concentration (at. %)
1%, 2%, 3%, 5%
Max length (mm)
50
Length tolerance (mm)
+0.5/-0.2
Aperture tolerances (mm)
+/-0.1
Parallelism
<30’’
Perpendicularity
<15’
Surface Quality
10/5
Coating
AR-coated
Reference.
[1] Qiangqiang Hu. Study on the growth and properties of several disordered structured crystals[D]. Shandong University, 2017.
[2] Su Xiancui. Study on femtosecond laser properties of ytterbium ion-doped LuAG, CLGA and CGA crystals [D]. Shandong University, 2018.
[3] Zhang Z B. Study on the growth and laser performance of Yb:YAG crystal [D]. University of Electronic Science and Technology, 2005.
[4] Druon F, Boudeile J, Zaouter Y, et al. New Yb-doped crystals for high-power and ultrashort lasers[C] // Optics / Photonics in Security and Defence. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2006:64000D-64000D-16.
[5]Druon F, Ricaud S, Papadopoulos N, et al. On Yb:CaF2 and Yb:SrF2: review of spectroscopic and themal properties and their impact on femtosecond and high power laser performance[J]. Optical Materials, 2011,489~502.
Previous page
Inquiry List